In this article, we will explore some of the most remarkable UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey, highlighting their significance and why they deserve to be protected for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
Turkey is a treasure trove of cultural and historical wonders, with a rich heritage that spans thousands of years. Among its many treasures are the UNESCO World Heritage Sites, which showcase the country’s outstanding universal value and contribute to humanity’s collective memory.
From ancient cities to natural landscapes, these sites offer a glimpse into Turkey’s diverse history and breathtaking beauty.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey
The people of the Balkans are warm and welcoming. They’re proud of their culture and history and always happy to share it with visitors. The food in the Balkans is delicious and diverse, and you’ll find something to suit every taste.
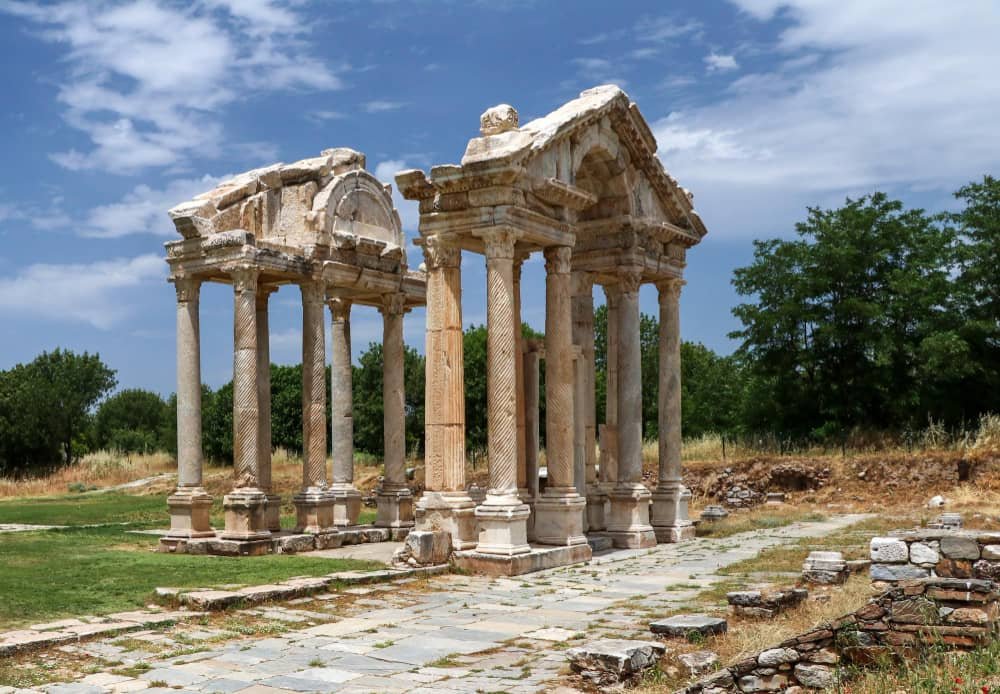

Aphrodisias
Located in the Aydın Province of Turkey, Aphrodisias is a captivating ancient city that is a testament to the region’s rich history and cultural heritage. Renowned for its well-preserved ruins and extraordinary craftsmanship, Aphrodisias has earned its place among the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
With its origins dating back to the 3rd century BCE, this archaeological marvel has thrived as a center for art, philosophy, and worship throughout various civilizations that have left their indelible mark on its grounds. Immerse yourself in exploring Aphrodisias and discover the allure of this remarkable site where mythological legends intertwine with historical significance.
Among the UNESCO World Heritage sites in Turkey is Aphrodisias, which encompasses the Temple of Aphrodite from the 3rd century BCE and the adjacent ancient marble quarries that had contributed to the prosperity of the ancient Greek city.

Arslantepe Mound
Arslantepe Mound, located in the Malatya Province of Turkey, is a remarkable archaeological site that has earned its place as one of Turkey’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites. This ancient mound, dating back thousands of years, holds invaluable insights into the region’s rich history. With its exceptional preservation and significant cultural significance, Arslantepe Mound is a testament to the thriving civilizations that once thrived in Anatolia.
As one explores this captivating site, it becomes evident why Arslantepe Mound was deemed worthy of such prestigious recognition by UNESCO. The mound showcases an extraordinary array of well-preserved structures and artifacts from various periods spanning roughly 6,000 years.
The first swords known in the Early Bronze Age were discovered at Arslantepe. These significant findings have shed light on the development of weaponry during this period and have been extensively studied by Marcella Frangipane from Rome University.
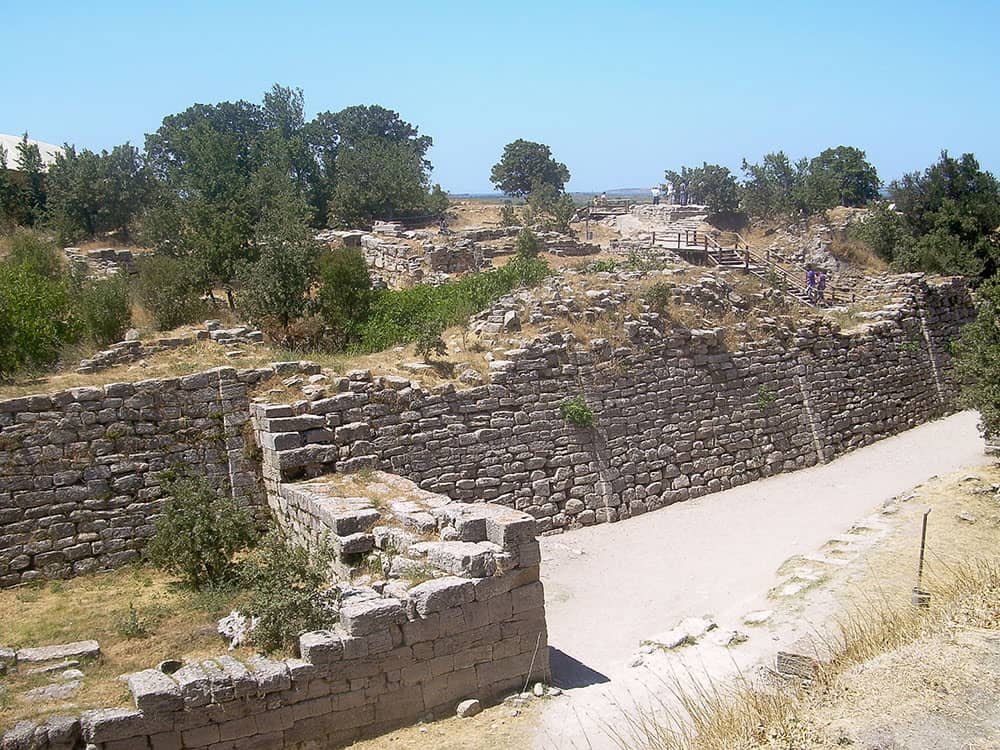

Archaeological Site of Troy
The Archaeological Site of Troy, located in the Çanakkale Province of Turkey, is a historically significant site that has captured the imagination of scholars and explorers for centuries. Designated as one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey, it stands as a testament to the ancient city immortalized in Greek mythology. It provides invaluable insights into the region’s rich cultural and historical past.
As visitors step foot on this hallowed ground, they are transported back to an era where heroes fought mythical battles and legendary tales were woven into reality. With its remarkable ruins and captivating stories, the Archaeological Site of Troy continues to be a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts from around the globe.
Heinrich Schliemann unearthed Troy in the late 19th century after it had been lost for over four millennia. Its significance as a major inspiration for Homer’s Iliad and Virgil’s Aeneid has made it one of the most renowned archaeological sites globally.
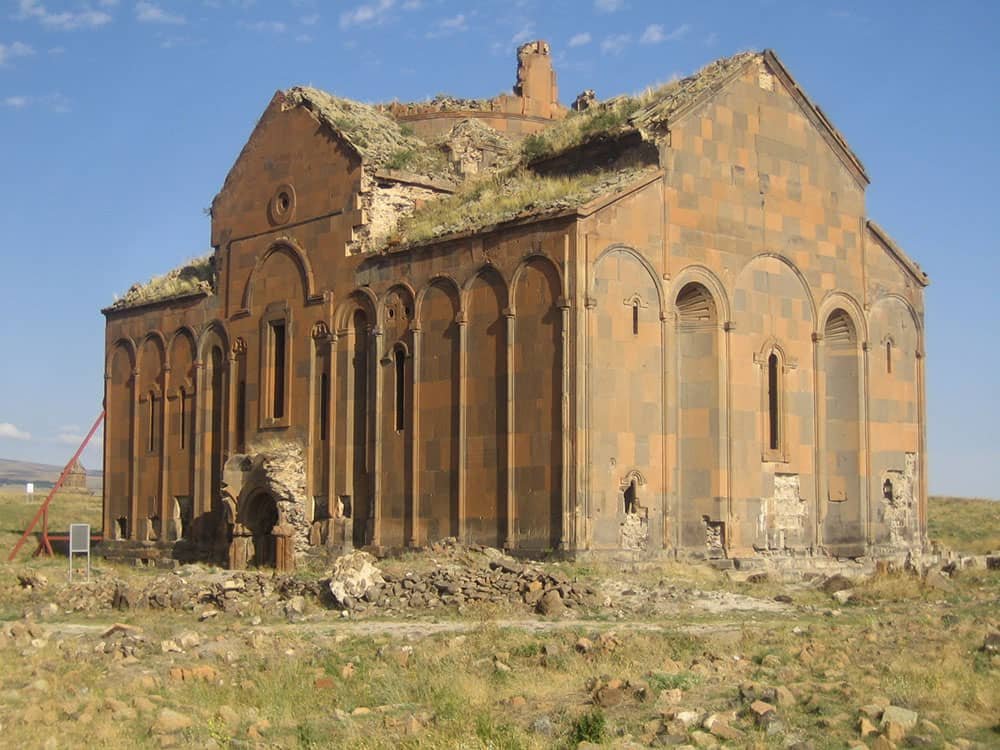

Archaeological Site of Ani
The Archaeological Site of Ani, located in the Kars Province of Turkey, is a remarkable testament to the region’s rich history and cultural heritage. As one of Turkey’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites, Ani stands as a symbol of human achievement and ingenuity, captivating visitors with its awe-inspiring architecture and archaeological significance.
This exceptional site offers a glimpse into the past, revealing the once-thriving medieval city once known as the city of 1,001 churches. Join us on a journey through time as we explore this incredible archaeological treasure trove and uncover its fascinating secrets.
Ani, an ancient city near the Turkey-Armenia border, experienced its peak during the 10th and 11th centuries as the capital of Bagratid Armenia. However, it gradually declined after the 14th century due to a Mongol invasion and a destructive earthquake.
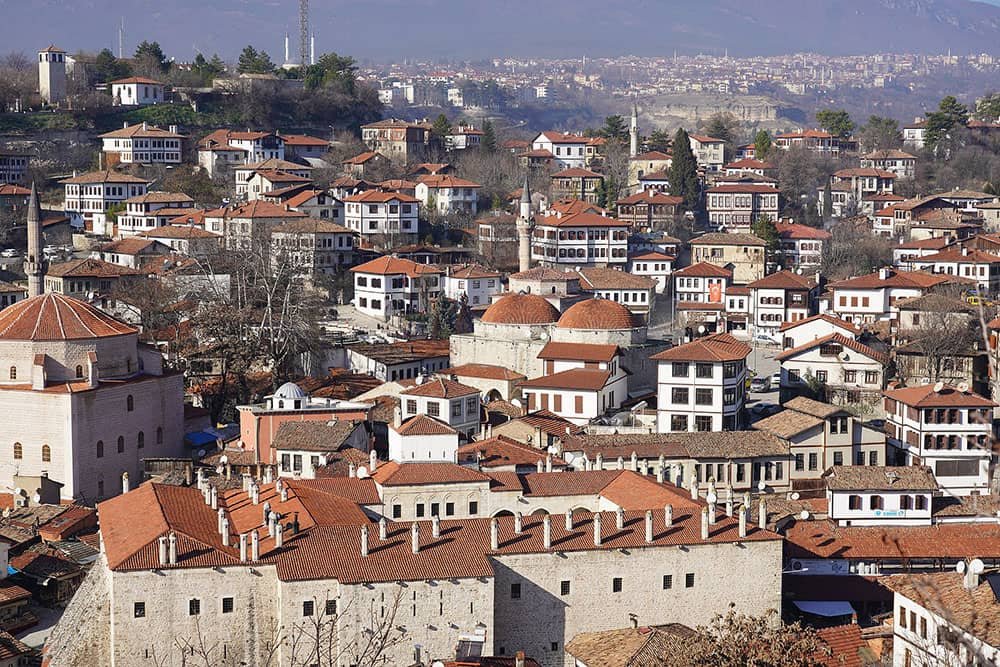

City of Safranbolu
Safranbolu, a captivating city in the Karabük Province of Turkey, boasts a rich history and cultural heritage, earning it the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage Site title. Situated amidst rolling hills and lush greenery, this enchanting destination offers a glimpse into Turkey’s past with its well-preserved Ottoman architecture and traditional way of life.
As one explores the cobblestone streets lined with centuries-old houses, mosques, and historic structures, it becomes apparent why Safranbolu is a treasure trove for history enthusiasts and architecture lovers alike.
Safranbolu, a hub for the caravan trade, experienced significant growth starting from the 13th century. The city’s unique architectural style played a crucial role in shaping urban development across the Ottoman Empire, leaving a lasting impact. This has led to Safranbolu being recognized as one of Turkey’s UNESCO World Heritage sites.
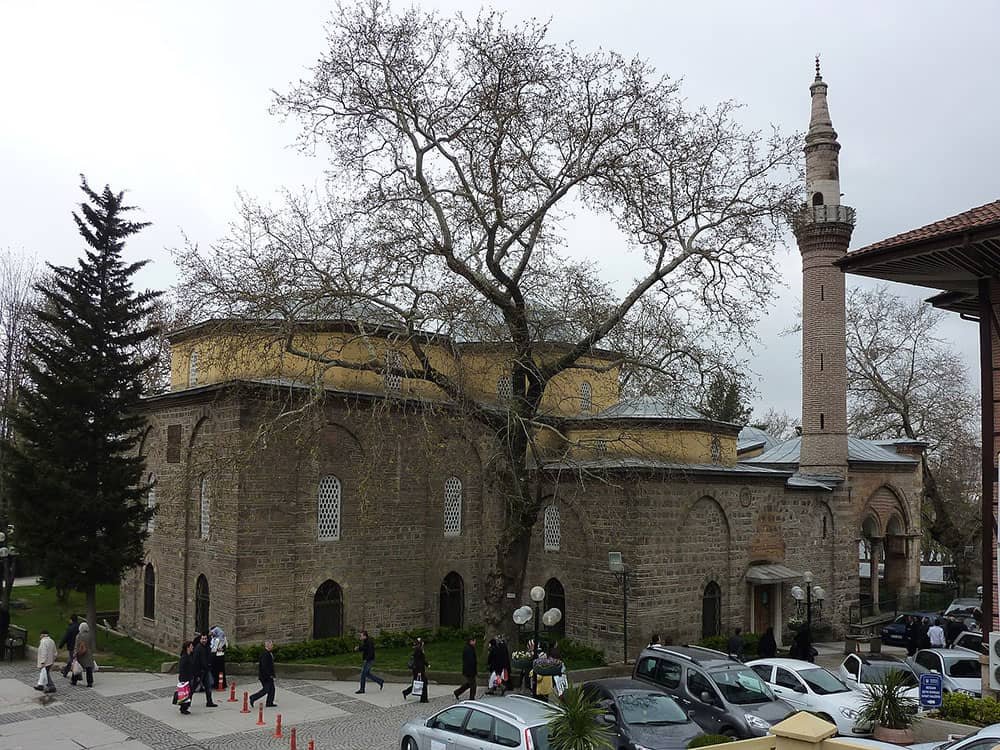

Bursa and Cumalıkızık: the Birth of the Ottoman Empire
Turkey is a treasure trove of historical sites, with its rich cultural heritage attracting millions of tourists annually. Among the countless gems adorn this ancient land, two UNESCO World Heritage Sites are significant in Turkey’s history: Bursa and Cumalıkızık. These sites showcase the architectural splendor of the Ottoman Empire and mark the birthplace of one of history’s most formidable empires.
Situated at the foot of Mount Uludağ in northwestern Turkey, Bursa is a testament to the grandeur and power amassed by the Ottoman Empire. Founded in 1299 by Osman I, this city was an influential political and economic center for centuries.
Due to its groundbreaking urban design, the Bursa was a significant model for forthcoming Ottoman cities. Additionally, the neighboring village of Cumalıkızık, which showcased the vakıf system, played a crucial role in supporting the capital city’s growth and progress.
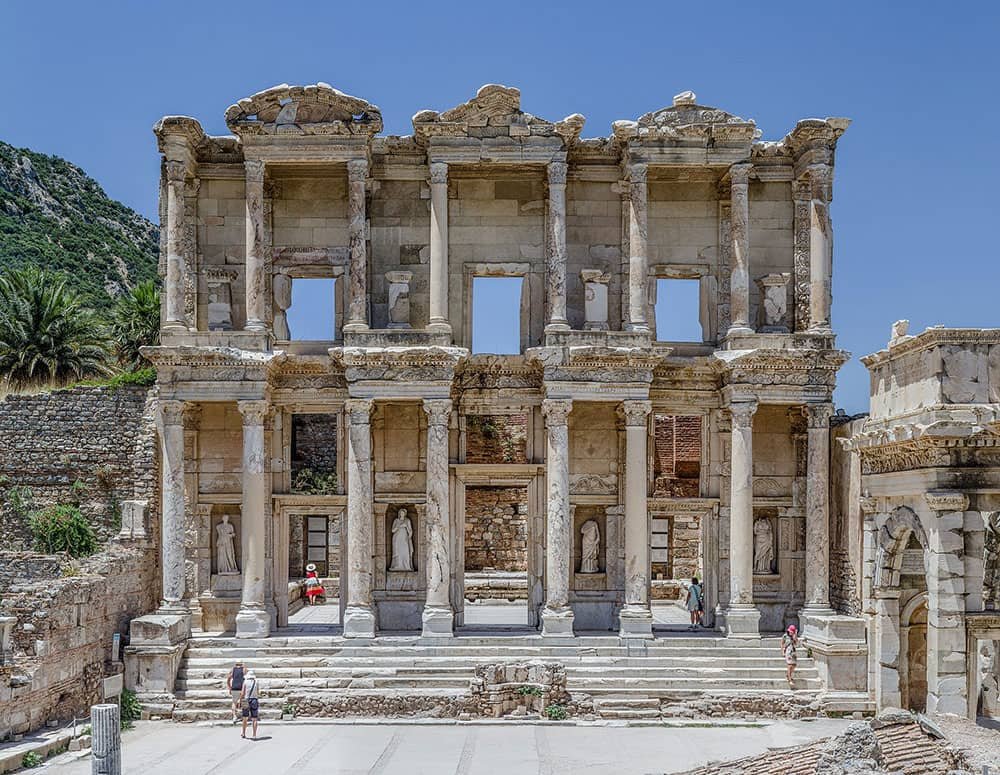

Ephesus
One of Turkey’s UNESCO World Heritage sites is the ancient Greek city of Ephesus, known for its renowned Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, now in ruins. Following its acquisition by the Romans in the 2nd century BCE, the city thrived and left behind impressive architectural marvels like the Library of Celsus.
Ephesus, located in the Izmir Province of Turkey, is a mesmerizing archaeological site that has captivated visitors worldwide. As one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey, its historical and cultural significance cannot be overstated. With its well-preserved ruins and grandeur dating back to ancient times, Ephesus stands as a testament to the rich heritage of this region.
Once an important city in ancient Greece and later under Roman rule, Ephesus flourished as a bustling metropolis renowned for its architectural marvels and commercial prosperity. Today, it is a remarkable open-air museum showcasing impressive structures such as the Library of Celsus, the Temple of Artemis, and the Great Theatre.
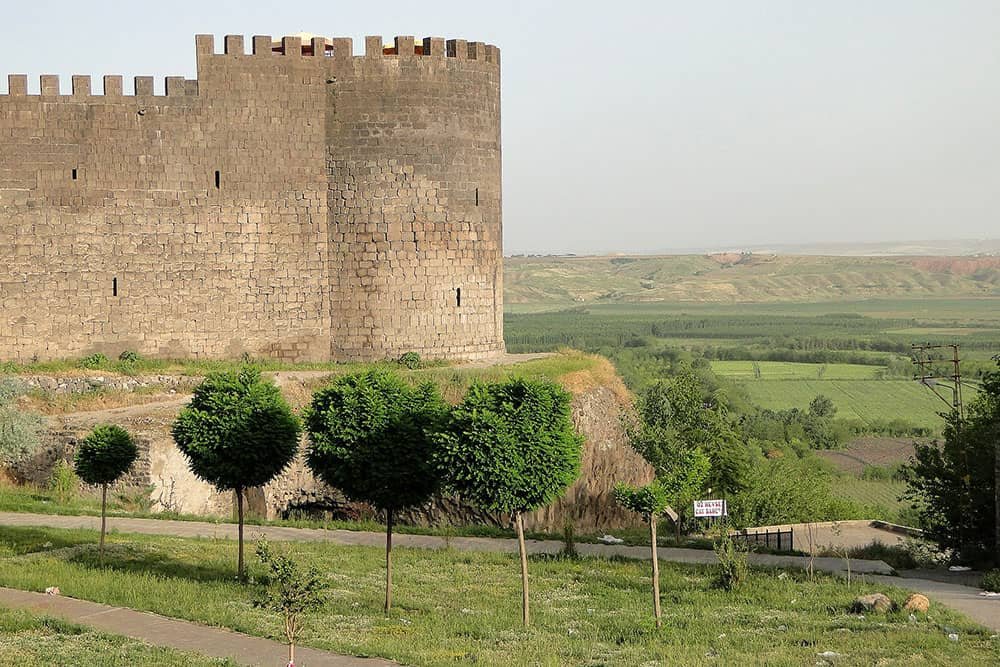

Diyarbakır Fortress and Hevsel Gardens Cultural Landscape
Diyarbakır Fortress and Hevsel Gardens Cultural Landscape in Turkey is a remarkable UNESCO World Heritage Site encompassing this ancient region’s rich historical and cultural heritage.
Nestled in southeastern Turkey, Diyarbakır Fortress stands tall as one of the most magnificent military structures in the world. The adjacent Hevsel Gardens present an awe-inspiring testament to human ingenuity and sustainable agricultural practices. Together, these sites offer a captivating journey through time, inviting visitors to explore the intricate tapestry of civilizations that have shaped this land for millennia.
Diyarbakır Fortress, also known as Amida Castle, is of great architectural significance. Its awe-inspiring walls stretch over five kilometers and are punctuated by numerous towers and gates.
Diyarbakır has held immense importance since the Hellenistic era and remains a notable city throughout history. Within its boundaries lie the remarkable 5.800km-long city walls of Diyarbakır, alongside the Hevsel Gardens, which have served as a vital source of sustenance and water for the city. These remarkable features have earned Diyarbakır a well-deserved place among Turkey’s UNESCO World Heritage sites.
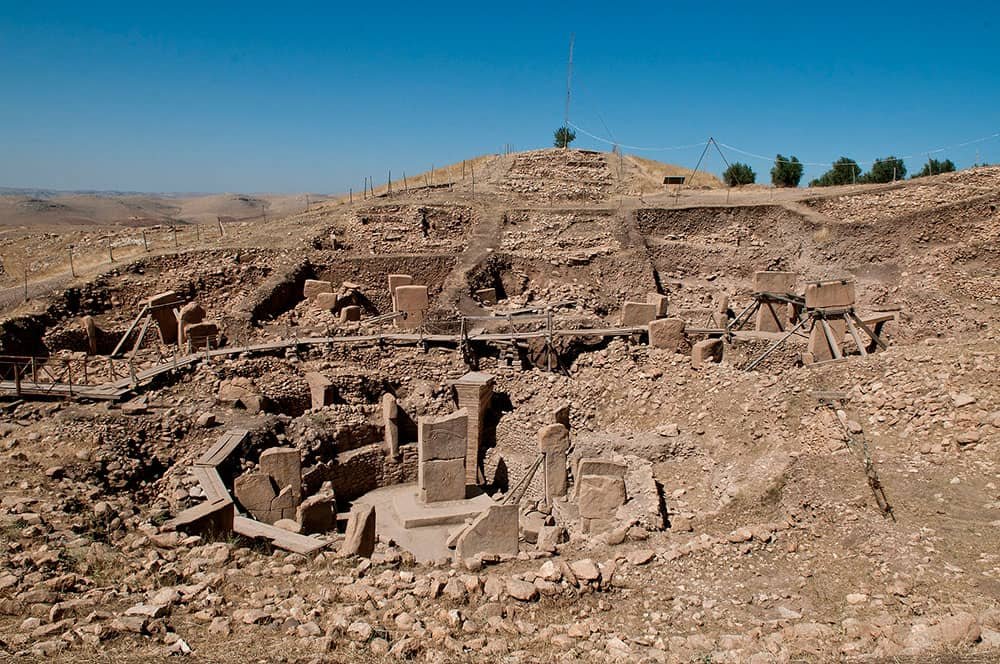

Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe, located in the Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, is an extraordinary archaeological site that has gained international recognition as one of the most significant ancient structures in the world. This captivating site, dating back to the Neolithic period, attracts researchers and tourists alike with its intricate stone carvings and monumental architecture. Added to the prestigious list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 2018, Göbekli Tepe is a testament to early human civilization’s ingenuity and complexity.
Situated on a barren hilltop overlooking the fertile plains of southeastern Turkey, Göbekli Tepe was discovered by German archaeologist Klaus Schmidt in 1994.
The site, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage site in Turkey, is believed to have been utilized by hunter-gatherers for ceremonial activities, dating back to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic age around the 10th and 9th millennium BCE.
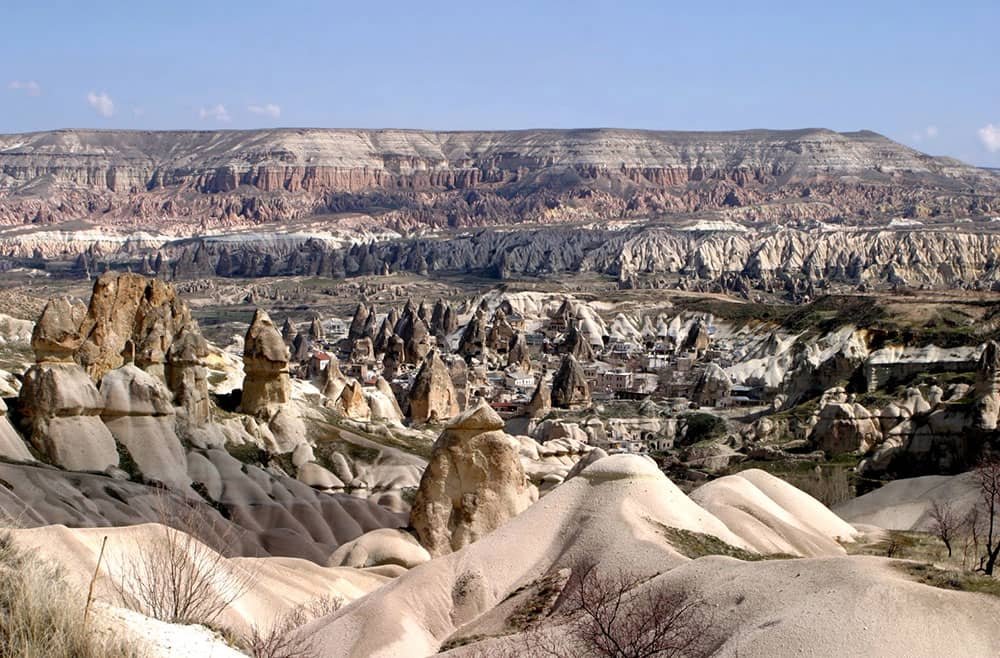

Göreme National Park and the Rock Sites of Cappadocia Turkey
Located in central Turkey, the Göreme National Park and the Rock Sites of Cappadocia are a testament to natural and cultural wonders. These unique sites have been recognized by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites, showcasing their immense historical and geological significance. Renowned for its otherworldly landscapes, these sites encompass an array of fascinating rock formations, ancient cave dwellings, and meticulously carved churches that date back thousands of years.
Göreme National Park and the Rock Sites of Cappadocia offer visitors a journey through time. Evidence of human habitation dates back to the 4th century BC.
The history of this region dates back thousands of years when volcanic eruptions blanketed the area with ash and created a soft stone known as tuff.
The remarkable hoodoo rock formations in the Greme Valley area have made it renowned. At the same time, the region of Cappadocia showcases an array of rock-hewn dwellings, villages, churches, underground cities, and exceptional post-Iconoclastic Byzantine art.
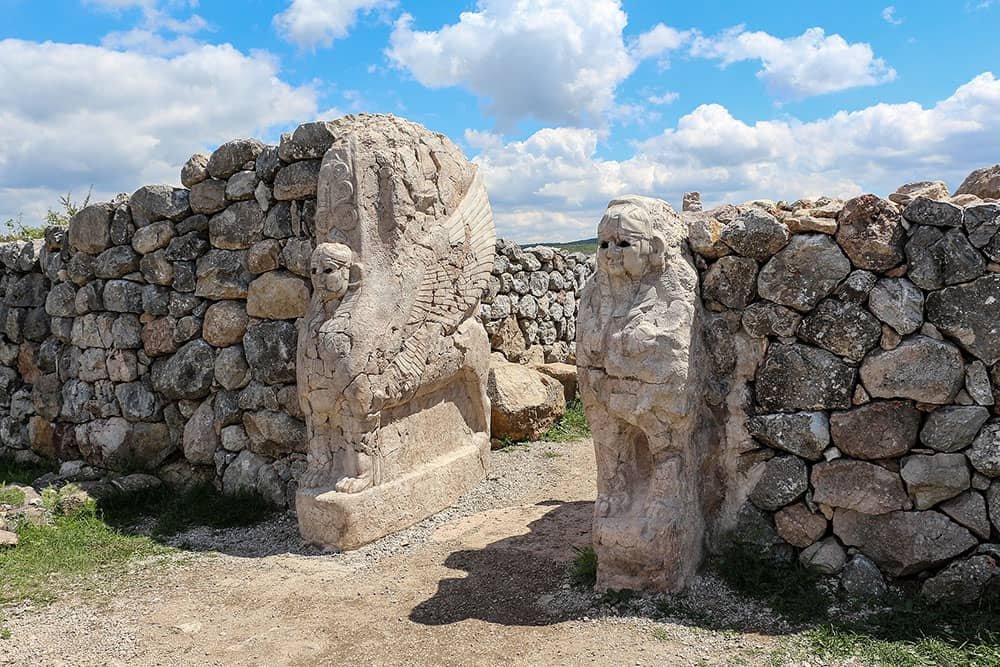

Hattusha: the Hittite Capital
Hattusha, a magnificent ancient city nestled in the Orum Province of Turkey, stands as a testament to the grandeur and power of the Hittite Empire. With its awe-inspiring ruins and rich cultural heritage, Hattusha has earned its place among the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
Visitors stroll through this historical marvel and are transported back to an era when this sprawling metropolis was the capital of one of antiquity’s most influential civilizations.
Situated on a rocky plateau surrounded by rugged hills, Hattusha was once a thriving center of political, economic, and social activity during the height of the Hittite Empire from approximately 1650 to 1200 BCE.
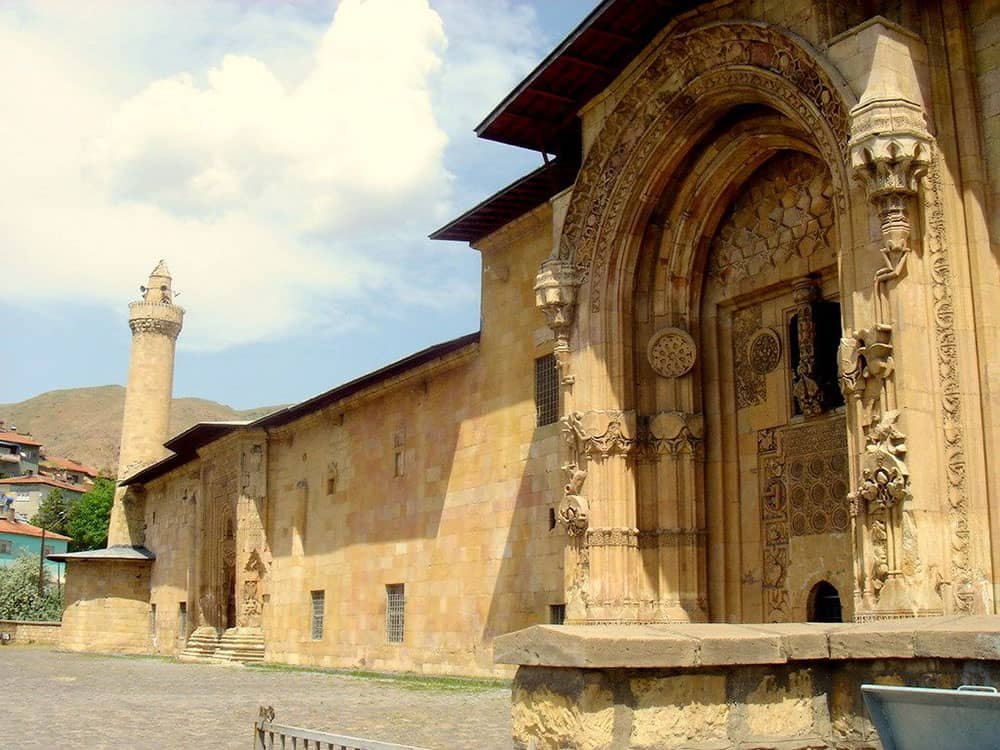

Great Mosque and Hospital of Divriği
The Great Mosque and Hospital of Divriği in Sivas Province, Turkey, testify to the region’s rich cultural heritage and architectural prowess. These remarkable structures have gained recognition on a global scale, earning them the prestigious designation of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
With their intricate designs and historical significance, the Great Mosque and Hospital exemplify the unique blend of Seljuk and Anatolian architectural styles that have left an indelible mark on Turkish history. The captivating history and exquisite features make these sites genuinely deserving of their UNESCO status.
The mosque-hospital complex at Divriği, stands as an exceptional and remarkable illustration of Islamic architecture, seamlessly integrating diverse and occasionally conflicting designs since its establishment in the early 13th century.
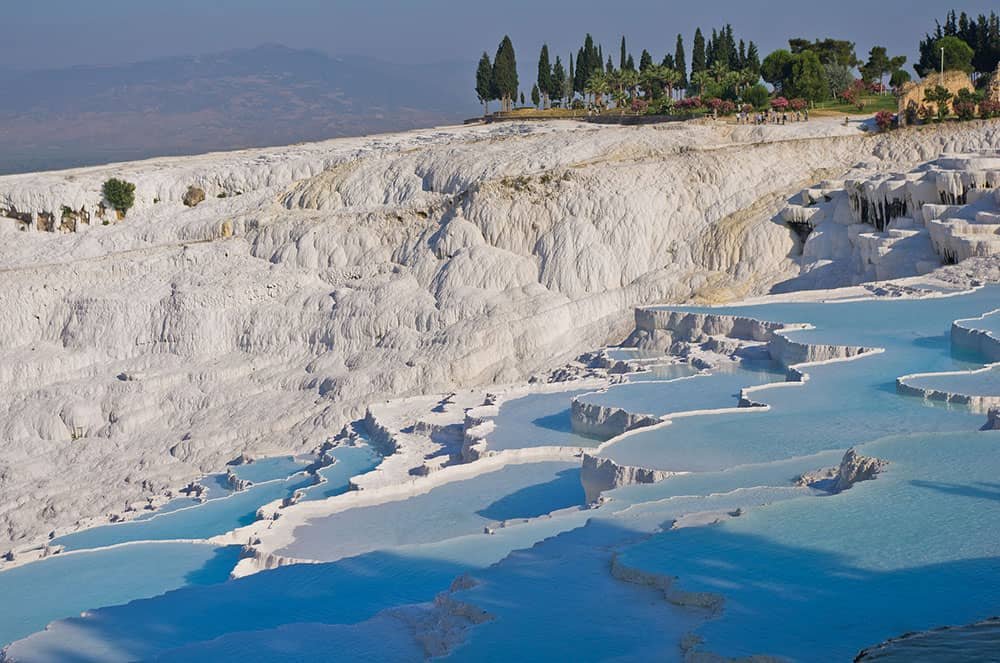

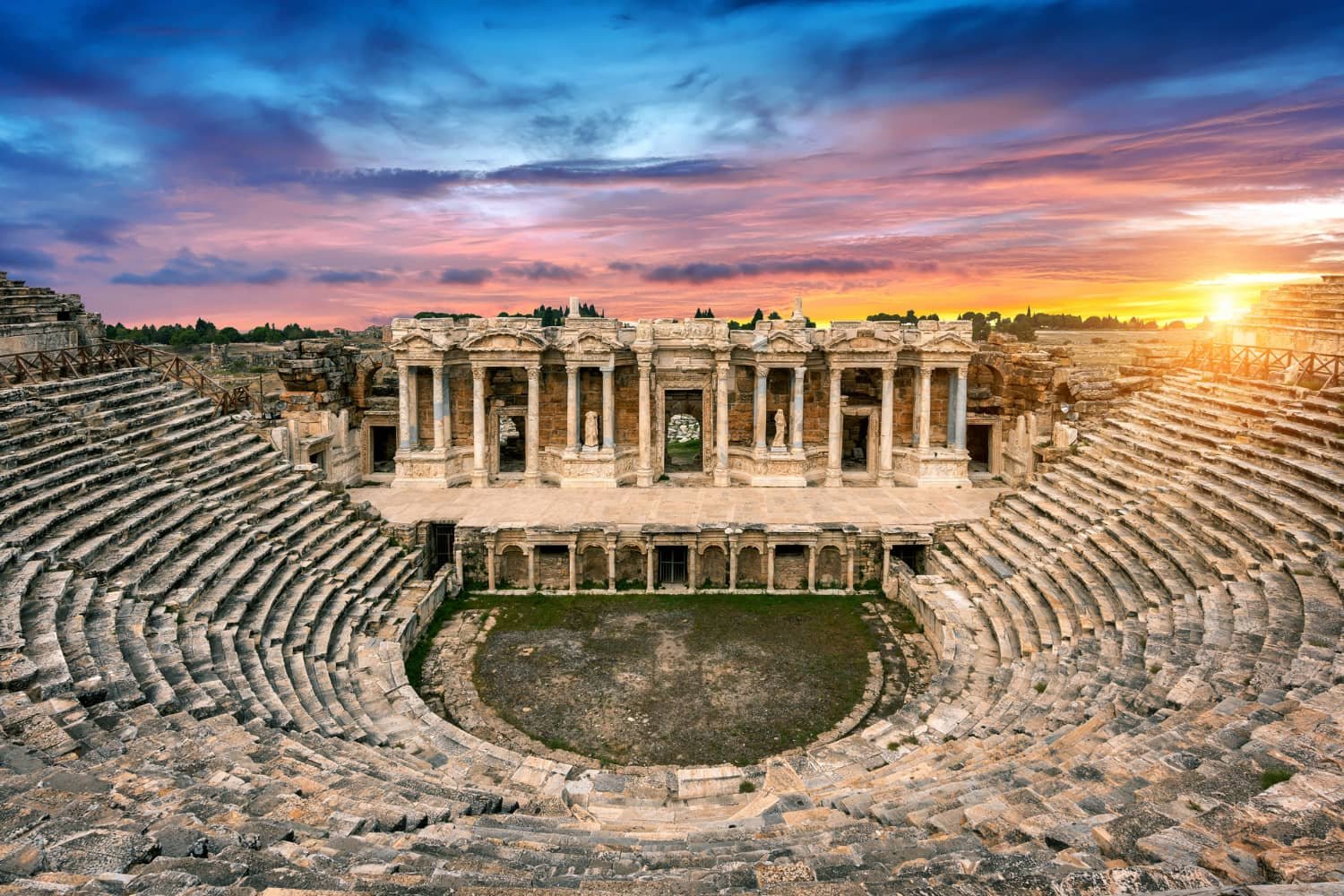
Hierapolis–Pamukkale
Hierapolis-Pamukkale is a captivating UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Denizli Province of Turkey. Renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty and historical significance, this remarkable destination offers visitors a unique blend of ancient ruins and stunning travertine terraces.
With its rich cultural heritage and mesmerizing landscapes, Hierapolis-Pamukkale stands as a testament to Turkey’s diverse historical legacy. It attracts travelers from around the globe who seek to immerse themselves in the wonders of this extraordinary site. Whether exploring its archaeological treasures or indulging in the therapeutic benefits of its thermal waters, a visit to Hierapolis-Pamukkale guarantees an unforgettable experience that seamlessly marries nature and history in one awe-inspiring location.
Pamukkale is renowned for its breathtaking scenery, characterized by petrified waterfalls, stalactites, and terraces. Adjacent to this natural wonder lies the town of Hierapolis, established in the late 2nd century BCE. It boasts an array of Greco-Roman structures, such as temples, baths, a necropolis, and even remnants of Early Christian architecture.
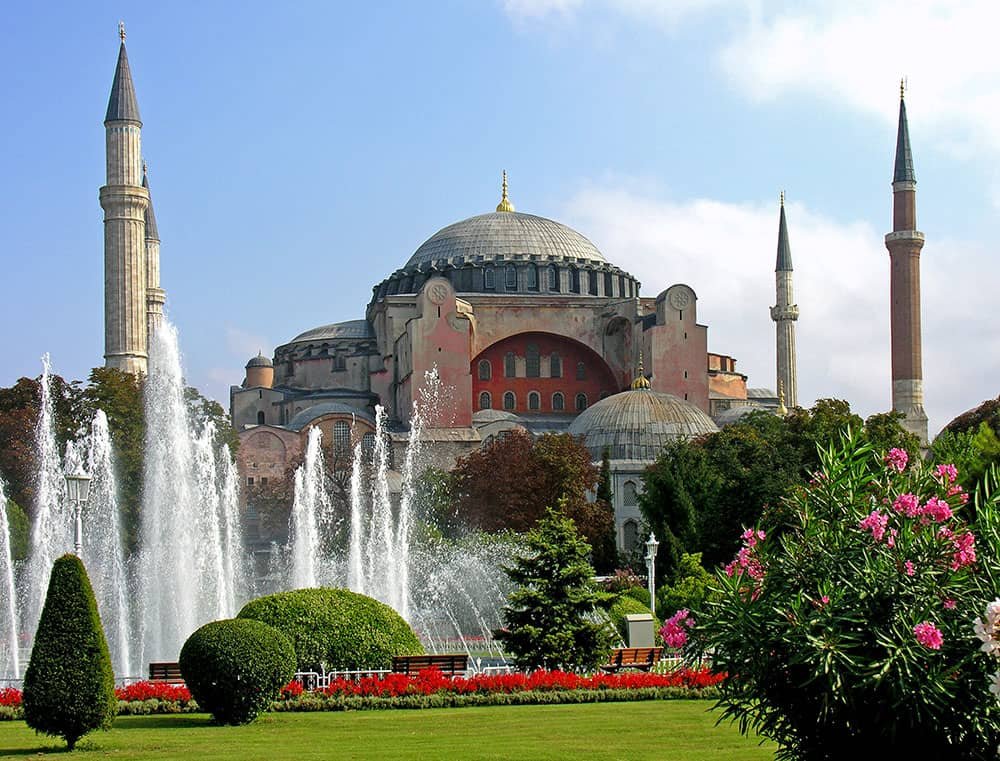

Historic Areas of Istanbul
Istanbul, the vibrant metropolis that straddles Europe and Asia, is steeped in history and cultural heritage. With its rich tapestry of civilizations and empires that have ruled over it throughout the centuries, Istanbul boasts an array of historic areas that are a testament to its illustrious past. These areas are significant to Turkey and the world, as they have been recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
From ancient ruins to majestic mosques, Istanbul’s historic areas encapsulate the diverse influences that have shaped this remarkable city. These sites serve as reminders of Istanbul’s pivotal role in connecting different civilizations and trade routes throughout history.
Istanbul, the former capital of the Byzantine and Ottoman empires, has played a significant role as a political, religious, and cultural hub for over two thousand years. Its remarkable architectural wonders, such as the Hippodrome of Constantinople, Hagia Sophia, Suleymaniye Mosque, and Topkap Palace, stand as a testament to the extraordinary talents of architects throughout history. These iconic landmarks are recognized as UNESCO World Heritage sites in Turkey.
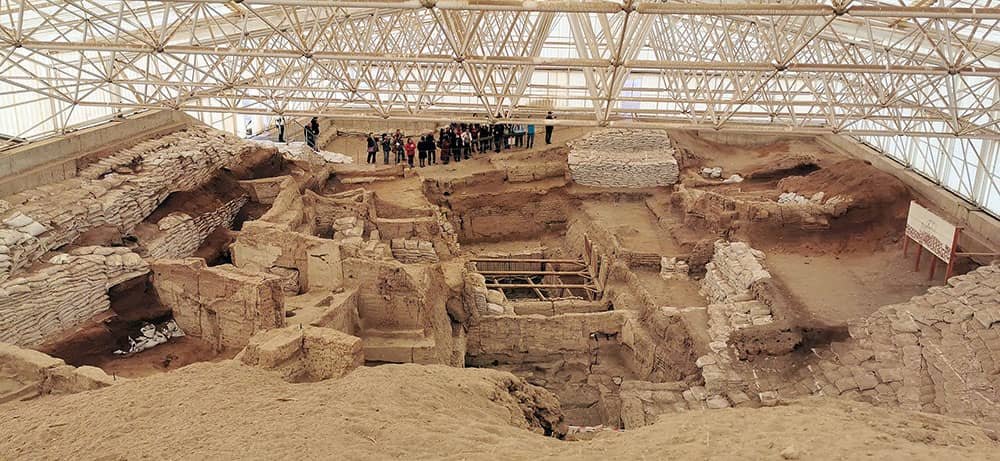

Neolithic Site of Çatalhöyük
The Neolithic Site of Çatalhöyük, located in the Konya Province of Turkey, is a remarkable archaeological site offering invaluable insights into early human settlements’ life and culture. Designated as one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey, this ancient city holds a significant place in human history.
The site’s exploration has unearthed an astonishing wealth of artifacts and evidence that shed light on the social, economic, and religious practices of its inhabitants, who lived approximately 9,000 years ago. With its well-preserved structures and unique architectural features, Çatalhöyük stands as a testament to the ingenuity and sophistication of Neolithic society while providing invaluable data for understanding our shared past.
Its urban design, inclusive housing with roof access, and wall paintings and reliefs provide evidence of a proto-urban lifestyle characterized by equality.
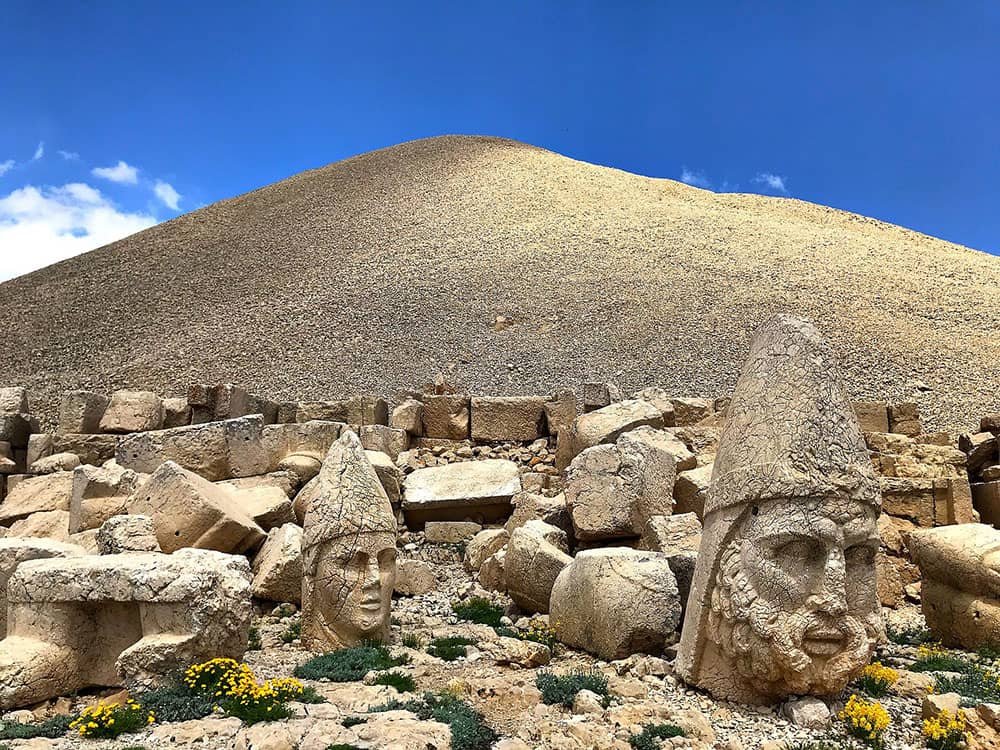

Nemrut Dağ
Nemrut Dağ in AdıyamanProvince, Turkey, stands as a magnificent testament to the region’s rich historical and cultural heritage. This awe-inspiring site has been honored with prestigious recognition as one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey. Nestled amidst the rugged landscape of southeastern Turkey, Nemrut Dağ epitomizes the fusion of ancient traditions, architectural grandeur, and spiritual significance.
Perched at an altitude of 2,134 meters (7,001 feet) above sea level, Nemrut Dağ is home to a series of monumental stone statues and colossal heads that once adorned a royal tomb complex dating back to the 1st century BC.
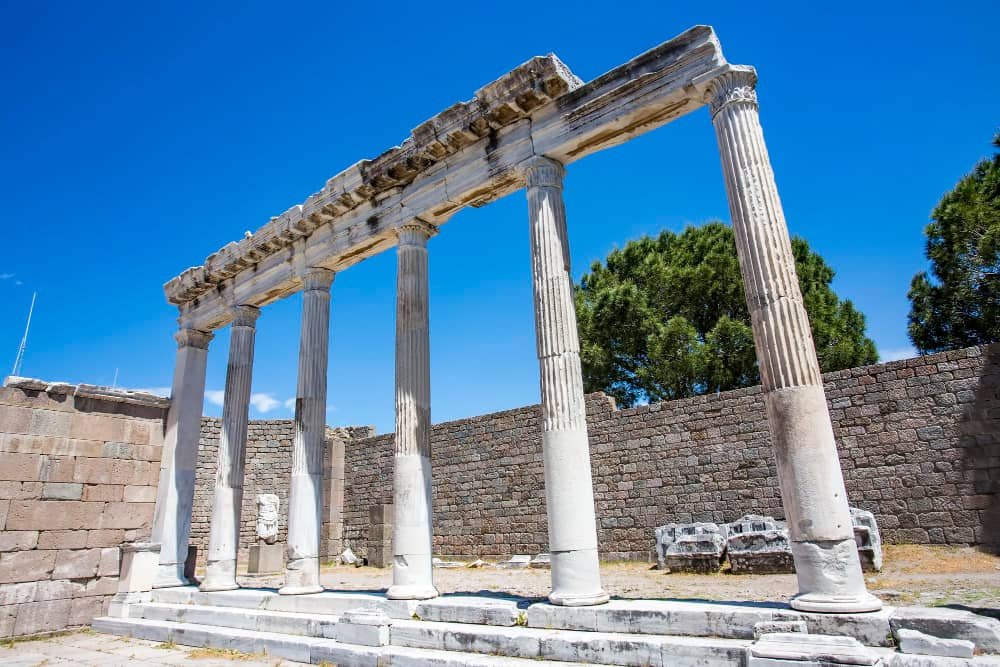

Pergamon and its Multi-Layered Cultural Landscape
Pergamon, situated in the İzmir Province of Turkey, is a captivating city that boasts a rich history and a multi-layered cultural landscape. Recognized as one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey, Pergamon offers visitors an immersive experience of ancient civilizations and diverse architectural wonders.
Whether you are an ardent history enthusiast or intrigued by world heritage sites, Pergamon promises to leave you awe-inspired with its remarkable blend of ancient ruins and natural beauty.
Pergamon was established in the 3rd century BC as the capital of the Hellenistic Attalid dynasty. It was significant in ancient times and flourished under Roman rule from 133 BC onwards, gaining recognition as a prominent healing hub.
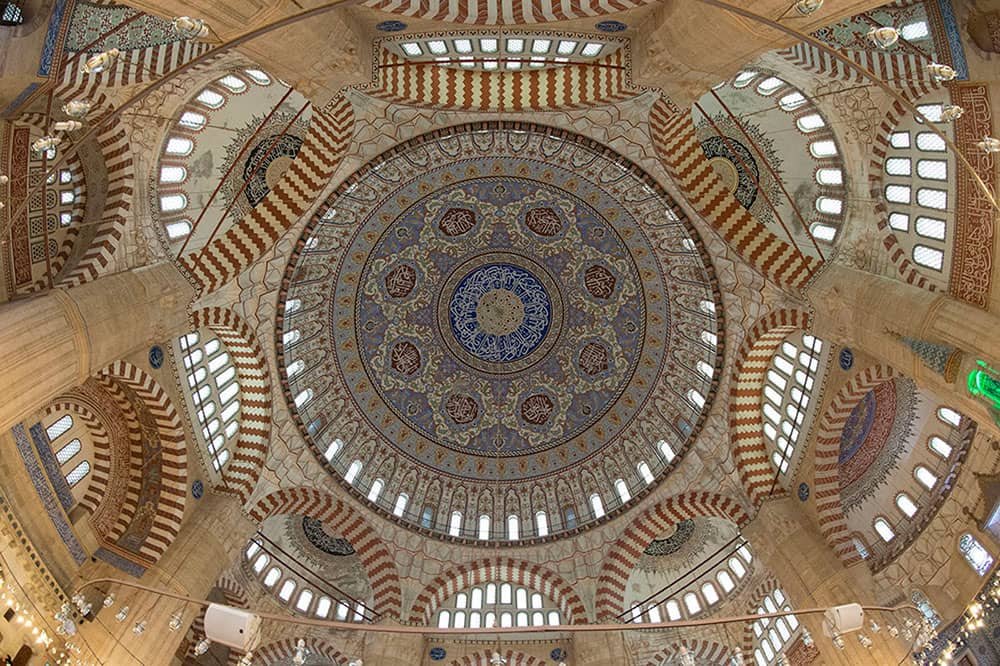

Selimiye Mosque and its Social Complex
Selimiye Mosque and its Social Complex in Edirne Province, Turkey, is a remarkable example of Ottoman architecture and cultural heritage. This awe-inspiring complex, located in the historic city of Edirne, has been recognized by UNESCO as one of the World Heritage Sites in Turkey. With its grand size, exquisite design, and rich historical significance, Selimiye Mosque continues to captivate visitors from around the globe.
Built during Sultan Selim II’s reign in the 16th century, Selimiye Mosque is considered a masterpiece of Mimar Sinan, one of history’s greatest architects. This architectural gem showcases the grandeur and magnificence typical of Ottoman mosques while incorporating unique elements that set it apart from others.
This architectural masterpiece served as a place of worship and functioned as a center for education, healthcare, and social welfare within the local community. With its intricate design elements, historical significance, and enduring legacy, the Selimiye Mosque continues to captivate visitors worldwide with its rich cultural heritage.
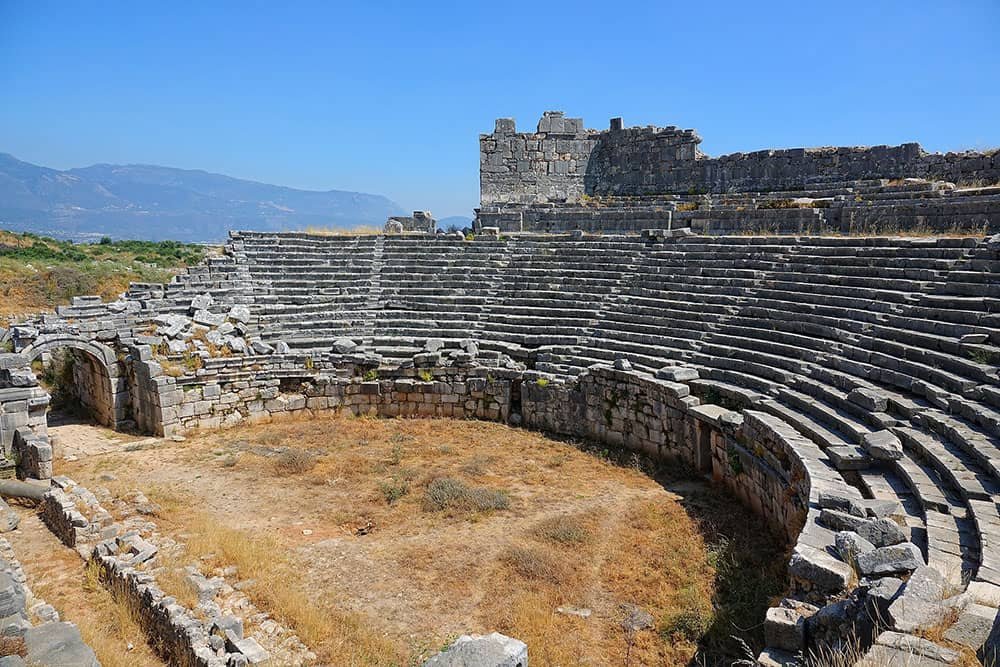

Xanthos–Letoon
Turkey is a country that boasts a rich historical and cultural heritage, with numerous UNESCO World Heritage Sites scattered across its vast landscape. Among these remarkable sites are the Xanthos-Letoon in Antalya and Muğla provinces, standing as testaments to the ancient civilizations that once thrived in this region.
These sites offer a glimpse into Turkey’s illustrious past and serve as reminders of the diverse influences that have shaped the country over centuries. With its exceptional universal value, Xanthos-Letoon proudly stands as an essential destination for history enthusiasts and curious travelers.
Xanthos-Letoon, located in southwestern Turkey, encompasses two distinct archaeological sites within proximity to each other.